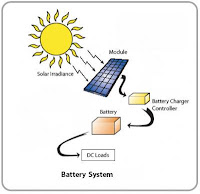
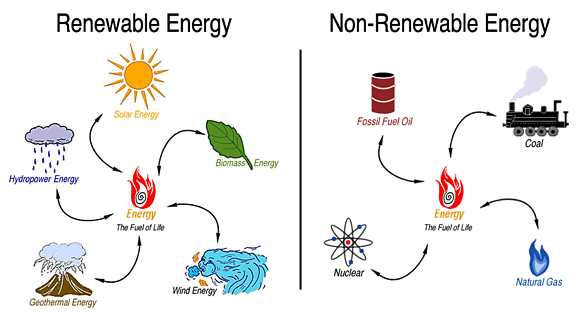
Chemical energy is stored in the particles that make up food, fuel, and other matter. Each of these atoms and molecules are held by strong or weak bonds. Chemical energy is release when these bonds are broken. Almost all reactions involve chemical energy reactions. Therefore, chemical energy comes from both renewable and non renewable as well as nuclear sources. For example, photosynthesis, cell respiration, batteries and food are examples of chemical energy. Our food we eat contains chemical energy, our bodies convert it to kinetic energy that allows us to walk, run and move. Since the law of energy conservation states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, it means that the form of the energy is the only thing that changes. The chemical energy transforms to other energy types.
 |
| Chemical energy is transformed to radiant and heat (thermal energy) the total amount of energy remains constant |
External links
http://www.ifpaenergyconference.com/Chemical-Energy.html
http://www.buzzle.com/articles/chemical-energy-examples-of-chemical-energy.html
http://www.choptankelectric.com/kids/energyfacts.html
http://www.waterfuelconverters.com/ChemicalEnergy.html